Shoulder pain is extremely common, and often caused by injuries to the rotator cuff. Rotator cuff injuries cause pain and discomfort even with normal activities or sleep.
What is a rotator cuff injury, and what are the symptoms
A rotator cuff injury is a condition that affects the four rotator cuff muscles and tendons in your shoulder. These tendons are responsible for movement of the shoulder and lifting things away from your body or over your head. Injuries can occur over time with a wear-and-tear pattern or from an acute trauma or injury while playing sports or falling. If these muscles and tendons become inflamed or torn, the rotator cuff doesn’t work properly, causing pain.
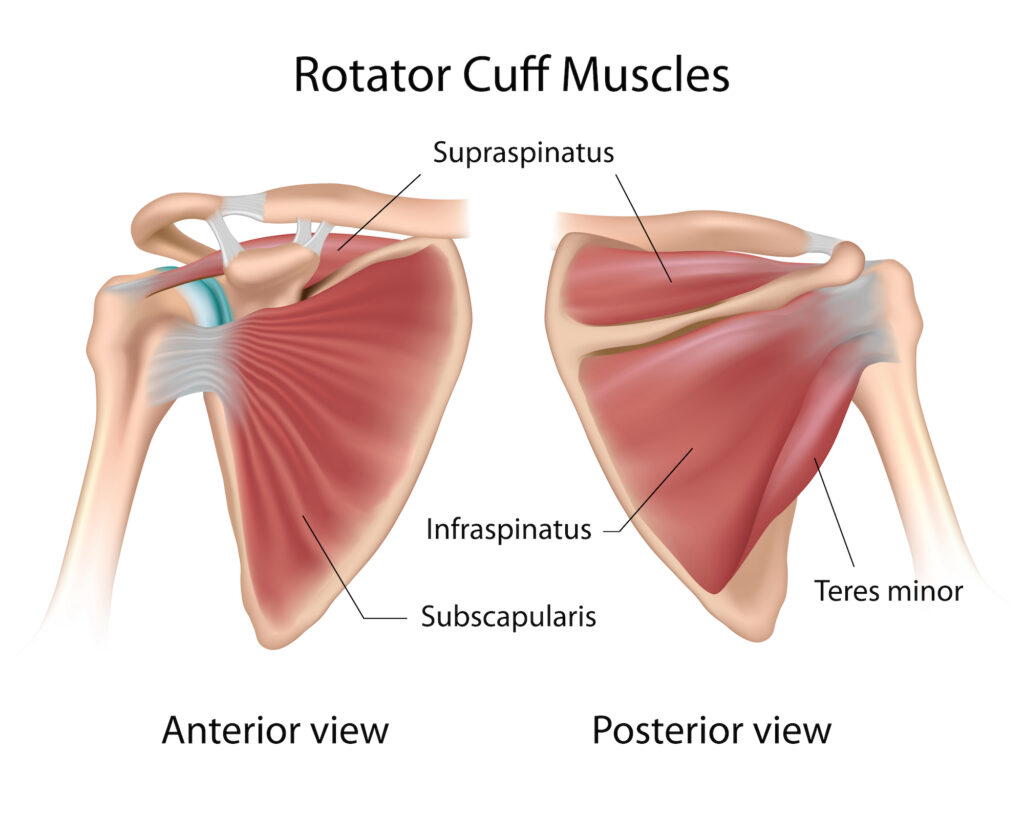
The symptoms of a rotator cuff injury can vary depending on the severity of the injury. In general, however, common symptoms include:
- Shoulder pain both in the front or side of the shoulder
- Reduced range of motion
- Pain when raising your arm overhead
- Pain at night or sleeping on your side
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you will want to see a shoulder specialist. Rotator cuff injuries can cause long-term damage if left untreated.
Causes of rotator cuff injuries
There are many different causes of rotator cuff injuries. Some of the most common include:
- Falls
- Heavy lifting
- Repetitive motions
- Sports injuries
- Chronic wear-and-tear
How to prevent rotator cuff injuries
There are several things you can do to prevent rotator cuff injuries from happening. Some of the most important include:
- Strengthening your rotator cuff muscles and tendons
- Stretching your shoulder muscles regularly
- Avoiding overuse or repetitive motions
Treatment options for rotator cuff injuries
The treatment options for rotator cuff injuries vary depending on the severity of the injury. In general, however, treatment options require and exam and MRI and may include:
Rest and ice packs – This can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Physical therapy – PT can help stretch and strengthen the muscles and tendons around the shoulder. It can also help improve range of motion.
Injections – Cortisone injections into the shoulder joint can be used to help reduce inflammation and pain. This is typically a temporary solution and should be used carefully as cortisone can lead to adverse effects to the joint.
PRP – It’s not uncommon to see patients where physical therapy and cortisone injections are a little too conservative but where surgery may be too aggressive. Some people with rotator cuff tears (partial tears) may be candidates for Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy. This is a treatment where your own blood is drawn and spun in a centrifuge to isolate the platelets. These platelets are concentrated and then injected into the tear to promote healing. Click here to read more about PRP applications in the shoulder.
Surgery – This is usually the last resort if other treatments are not working. It may include repairing torn tendons or removing bone spurs that are interfering with movement. Almost all rotator cuff repairs are performed in a minimally invasive manner (arthroscopically), which is much less invasive than traditional open surgery.
When to see a shoulder specialist
If you are experiencing shoulder pain or discomfort that is not improving, you should schedule an appointment with a shoulder specialist. Again, if left untreated, rotator cuff injuries can cause long-term issues, not to mention a decreased quality of life.
